What are Arithmetic Operators in Excel?
Arithmetic Operators are used to perform arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication and division etc. There are following arithmetic operators in Microsoft Excel:
 |
| Using Arithmetic / Mathematical Operators in MS Excel Formulas |
1. + Operator
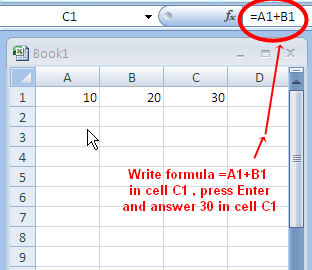
The + arithmetic operator is used to perform addition of numbers. It is used with in formulas along with Cell References normally. For example, to add the number 10 in A1 cell and the number 20 in B1 cell, we can write a formula =A1+B1 in cell C1. After pressing Enter key we will see the answer 30 in the cell C1.
Important Points To Write a Simple Formula in Excel
- Every formula in Microsoft Excel is started with an Equal sign ( = ).
- Arithmetic operators (+ for addition, - for subtraction, * for multiplication, / for division) are used.
- Percentage is calculated by % operator. ( =B2*10% means 10% of the number in cell B2)
- Power function is performed by ^ operator. (3^2 will give 9)
2. - Operator
The - arithmetic operator is used to perform subtraction of numbers. It is used with in formulas along with Cell References normally. For example, to subtract the number 100 in B1 cell from the number 50 in A1 cell, we can write a formula =B1-A1 in cell C1. After pressing Enter key we will see the answer 50 in the cell C1.
3. * Operator
The * arithmetic operator is used to perform multiplication of numbers. It is used with in formulas along with Cell References normally.
For example, to multiply the number 10 in A1 cell with the number 20 in B1 cell, we can write a formula =A1*B1 in cell C1. After pressing Enter key we will see the answer 200 in the cell C1.
4. / Operator
The / arithmetic operator is used to perform division of numbers and gives quotient of the division. It is used with in formulas along with Cell References normally.
For example, to divide the number 10 in A1 cell by the number 5 in B1 cell, we can write a formula =A1/B1 in cell C1. After pressing Enter key we will see the answer 2 in the cell C1.
5. % Operator
The % arithmetic operator is used to calculate percentage. It is used with in formulas along with Cell References normally.
For example, to calculate the 10 % of the number 1000 in A1 cell, we can write a formula =A1*10% in cell B1. We will read the formula =A1*10% as "10% of A1" means 10% of the number in cell A1. After pressing Enter key we will see the answer 100 in the cell B1.
6. ^ Operator (Exponent operator or Power operator)
The ^ arithmetic operator is used to calculate a number n raised to the power p. For example 2^3 is equal to 8 ( 2 raised to the power 3).
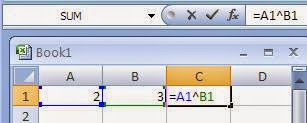
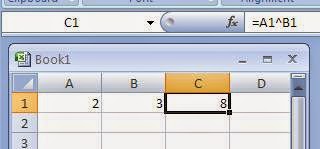
It is used with in formulas along with Cell References normally. For example, to calculate 2 raised to the power 3, type 2 in Cell A1 and 3 in cell B1. Now we can write a formula =A1^B1 in cell C1. After pressing Enter key we will see the answer 8 in the cell C1.
Order of Precedence of Arithmetic Operators in Excel
Order of precedence means the order in which operations will be performed when evaluating an expression in Microsoft Excel.
1. First of all the operation in parentheses ( ) is performed if any. If nested parentheses exist in expression, then the inner most parentheses will be evaluated first.
2. Secondly, Exponents will be evaluated if any.
3. In third step, multiplications and divisions will be calculated from left to right order.
4. In fourth step, additions and subtractions will be performed in Left to Right order.
Example: Evaluate the following expression according to the order of precedence in Excel
=A1*B1-C1*(20+3)
Solution: Let A1=10, B1=5, C1=2
Step 1. First of all parentheses (20+3) is evaluated to 23
Now expression becomes =A1*B1-C1*23
Step 2. Now there is no exponents, so we check multiplication and division. There are
two multiplication operators. Since A1*B1 is on left so we evaluate it by putting values
10*5 the answer is 50. Therefore expression is reduced to =50-C1*23
Step 3. Now we will evaluate multiplication C1*23. Putting values 2*23 and the answer is
46. So the expression becomes 50-46.
Step 4. Now we will evaluate the last operation of subtraction 50-46 which gives the answer 4.










Comments