Today, we will types of network topology.
What is a Network Topology?
Definition of Network topology is the shape of the network. It is the physical layout of connected devices in a network. It tells us how a network will look like.Network Topology ( Definition 2): The way in which the connections are made among all the network entities is called the topology of the network.
Network Topology ( Definition 3):Network topology specifically refers to the physical layout of the network, e.g., the location of the computers and how the cable is run between them.
Network Topology ( Definition 4):The physical topology of a network refers to the configuration of cables, computers, and other peripherals.
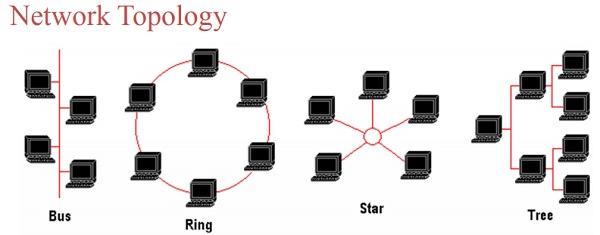 |
| types of network topology |
Explain different types of network Topology
Different network topologies are as follows:1. Bus Topology
2. Ring Topology
3. Star Topology
4. Tree Topology
5. Mesh Topology
1. Bus Topology

Bus topology is the simplest network topology. In bus topology, all computers in network are connected to a common communication wire. This wire is called BUS. Terminators are used at both ends of wire.
 |
| Bus Topology - Different Types of Network Topology |
2. Star Topology
Star Topology is the most popular and widely used network topology in local area networks. In star topology, all computers are connected with a central device known as HUB or Switch. Now-a-days Hubs are often replaced by Fast Network Switches. The sender computer sends data to the hub. The hub sends it to the destination computer. So, all data communication is managed through HUB or Switch. |
| Star Topology - Different Types of Network Topology |
Note: The major difference between a Networking Hub and Networking Switch is that HUB sends data to all computers, and the destination computer will accept it while other computers will not. On the other hand, Switch sends data only to the destination computer. Therefore, switch can reduce network traffic and hence provides fast transmission speed.
3. Ring Topology
In Ring topology, each computer is connected to the next computer such that last computer is connected to the first. Every computer is connected to next computer in the ring. Each computer retransmits what it receives from the previous computer. Suppose, computer A needs to send data to computer D. Now the computer A sends data to computer B. As computer B is not the destination computer, so it will retransmit data to computer C. Finally, Computer C will transfer data to computer D, the destination computer. When a node sends a message, the message is processed by each computer in the ring. If a computer is not the destination node, it will pass the message to the next node, until the message arrives at its destination. |
| Ring Topology - Different Types of Network Topology |
4. Tree Topology
Actually, a Tree topology is the combination of two topologies: bus and star topology. A tree topology combines the characteristics of bus and star topologies. It consists of groups of computer connected as star topology. These groups are then connected to a central communication medium (bus cable). |
| Tree Topology - Different Types of Network Topology |
5. Mesh Topology
In a mesh topology, every device on the network is physically connected to every other device on the network. Therefore, data can be sent on several possible paths from source computer to destination computer. Mesh topology is more reliable with better performance. It is mostly used in wide area networks where reliability is important. |
| Mesh Topology - Different Types of Network Topology |
Comments
Aquiesse Frankincense & Myrrh Candle
Thanks for being here. Sure, you can share some of this stuff on your blog, but don't forget to have a link back to my blog. http://forfreeeducation.blogspot.com