Today we will discuss some important basic Microsoft Office Word Processing Practicals. These practicals are essential part of Learning Microsoft Word for basic documentation preparation process.
Start Microsoft Word according to the procedure shown in the following picture or by double clicking the Microsoft Word shortcut on desktop.
Microsoft Word will open with a blank document.
Type something in this Word document
Then Click on Microsoft Office button and then Save option
Or you can press keyboard shortcut CTRL+S
Type file name and select location
Click on Save.
I have given the solutions according to some old versions of Microsoft Office 2000, 2003 etc.
How To Create a New File (Document) and Save It
Start Microsoft Word according to the procedure shown in the following picture or by double clicking the Microsoft Word shortcut on desktop.
Microsoft Word will open with a blank document.
Type something in this Word document
Then Click on Microsoft Office button and then Save option
Or you can press keyboard shortcut CTRL+S
Type file name and select location
Click on Save.
I have given the solutions according to some old versions of Microsoft Office 2000, 2003 etc.
MS OFFICE 2000, 2003 Old is Gold

Open Microsoft Word
Start -> Programs -> Microsoft WordTo Create a New File
File -> New or Press CTRL+N
To Save a File:
File -> Save or Save As -> Type file name -> Select file location -> click on SaveTo Save a File with Password
File -> Save As -> Click on Tools -> General Options -> Type password in Password to open box.-> Ok -> Retype password / confirm password -> ok -> save
To Save Document in a Folder on Desktop
File -> Save As -> Select Desktop -> Click on New Folder button on dialogue box ->
Type folder name -> Type filename -> Save
Some More Useful Features for Microsoft Office Word Processing Practicals
How to set Paragraph Line Spacing
Type Paragraph. -> Select paragraph
-> Press
CTRL+1 For single line spacing
CTRL+2 For double line spacing
CTRL+5 For 1.5 line spacing
Text Effects
Select text -> Format menu -> Text Effects Tab -> select a text effect -> ok
Change Case
Select text -> Format -> change case -> select option -> ok (short cut CTRL+F3)
Borders and Shading
Select paragraph -> Format menu -> Borders and shading -> borders tab
-> Select a border setting, style, color and width -> ok
Shading
Select paragraph -> Format menu -> Borders and shading -> shading tab
-> Select a color from fill section -> ok
Microsoft Office Word Processing Practicals: Applying Graphical Page Borders
Page Borders
Format menu -> Borders and shading -> Page Border tab
-> Select a border from Art list box -> set other options -> ok
DROP CAPS
Image for Drop Caps Microsoft Office Word Processing Practicals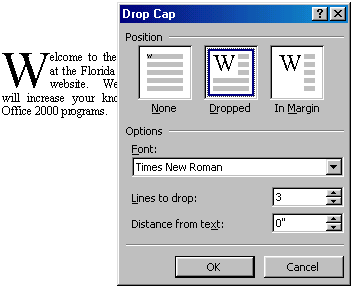
Place the cursor in paragraph -> Format menu -> Drop Caps -> select different options -> ok
Header and Footer
Picture for Header and FooterView Menu -> Header and Footer -> Type text in header or use Insert Auto text option to
enter different options like Page X of Y --- Page 1 of 10 --- etc
-> click on Switch between header and footer button -> type text in footer or insert page number
etc. -> Close
Insert Page Number
Insert Menu -> Page Number -> set different options -> ok
Microsoft Office Word Processing Practicals: Inserting Word Art and Clip Arts
Word Art
Insert menu -> Picture -> Word Art -> set different options -> ok
Clip Arts
TABLES
Table menu -> Insert -> table -> select number of rows and columns
-> ok
TYPE Text E = mc2(Superscript and Subscript by Shortcut Key)
type the text E = mc2 -> select 2 -> press[ CTRL + Shift + = ]for super script text
similarly Press CTRL + = for subsript text
Bullets and Numbering
Select text -> Format menu -> bullets and numbering -> select bulleted or numbering tab ->
select bullets and number style
COLUMNS
Format menu -> columns -> select number of columns -> or select preset options
-> ok
Soon, I will provide the same procedures to perform Microsoft Office Word Processing Practicals
in latest versions of MS Office.





Comments