Topic: Different Functions Of Operating Systems
An operating system can be defined as software that acts as an interface between the end user and the hardware. Computer users can use computer systems that have an OS or operating system installed. For example, Microsoft Windows is a popular PC operating system.
Similarly if you wish to install application programs like games, Microsoft Word, Firefox or Chrome web browser etc. you will install them with the help of the Operating system.
You can etcfolders, files etcIf you want to work on your computer, you must install an operating system on your computer.
When you start your computer, the operating system loads into the computer memory and appears as a user interface. The user can now work on a computer using this user interface provided by the operating system.
Following are the 14 main functions performed by Operating System:
You can create and save files and folders, edit files, copy files, move files from one location to another within one computer or from computer to computer, and delete files and folders etc, with the help oif operating system.
Topic: Different Functions Of Operating Systems
What is an Operating System?
Operating systems are an important type of system software. They provide a lot of facilities to the users.An operating system can be defined as software that acts as an interface between the end user and the hardware. Computer users can use computer systems that have an OS or operating system installed. For example, Microsoft Windows is a popular PC operating system.
What is the Importance of Operating System in Computer?
Each computer must have at least one operating system to run other programs. for example, if there is no operating system in your computer, you will not be able to use the computer. When you install an OS like Microsoft Windows on your computer, it displays its GUI that is Windows desktop on startup. Now you can use your computer with the help of graphical user interface elements like icons, menus, shortcuts on your computer screen.Similarly if you wish to install application programs like games, Microsoft Word, Firefox or Chrome web browser etc. you will install them with the help of the Operating system.
You can etcfolders, files etcIf you want to work on your computer, you must install an operating system on your computer.
When you start your computer, the operating system loads into the computer memory and appears as a user interface. The user can now work on a computer using this user interface provided by the operating system.
 |
| Different functions of operating systems |
Following are the 14 main functions performed by Operating System:
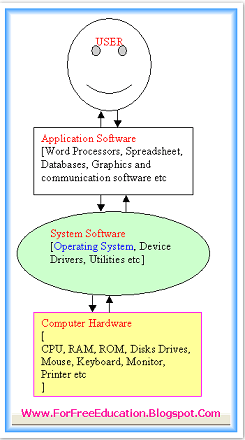 |
Explain Different Functions of Operating System |
1. Process Management
CPU can perform one task at one time. If there are many tasks, operating system decides which task should get the CPU first. Operating system also maintains a queue of jobs for processing one by one.2. Main Memory Management
Operating system manages memory (RAM)for many running programs. It allocates memory area to different programs. It de-allocates the memory area when a program is terminated. It also manages efficient use of RAM during processing.3. Secondary Storage Management
Operating system manages secondary storage. It manages the stored files and folders on disk in a proper way.You can create and save files and folders, edit files, copy files, move files from one location to another within one computer or from computer to computer, and delete files and folders etc, with the help oif operating system.
4. I/O System management
It manages Input/output operations. It controls I/O devices like mouse, keyboard, monitor and printer etc.5. File Management
It manages files, for example:- creation of files
- deletion of files
- copying of files.
- editing files
- moving of files etc.
6. Protection System
There are many processes of different users in memory at a time. So operating system provides protection so that no process can interfere with another process activity. Operating system makes sure that each and every process performs within its own boundaries.7. Networking
Operating system provides access to shared resources by networking system. Users can share files and hardware resources like printer.8. Command Interpreter system
Operating system provides command interpreter for reading and executing user commands. For example, Microsoft Windows XP provides Command Prompt to enter and execute commands.9. Booting
Operating system starts the computer. It checks the computer and makes it ready to work.10. Loading and Execution
Operating system provides the facility to load programs in memory easily and then execute it.11. Data Security
Operating system protects the data stored on the computer from illegal use, modification or deletion.12 Device Controlling
Operating system controls all devices attached to computer with the help of device drivers. Device driver is a software that permits a computer system to communicate with a device. e.g., device driver software for a modem comes with it on CD. We have to install device driver before using a device.13. Printing Controlling
Operating System also manages and controls printing function. If a user issues two or more print commands at a time, it manages print queue for printing each document one by one in a proper sequence.14. Providing User Interface
Operating system provides User interface to interact with the computer. User Interface may be Graphical user interface (GUI) or Command line interface. For example, Microsoft Windows XP provides an easy to use graphical user interface called GUI. Whereas DOS provides a Command Line Interface called CLI.Topic: Different Functions Of Operating Systems
Comments
Church Software